Varicose veins are a disease of the veins, which is manifested by their expansion, lengthening with the formation of nodules and thinning of the vein wall. It can affect various vessels but is most common in the lower extremities.
In advanced cases, this leads to trophic disorders in the affected area, the development of ulcers, eczema, and even necrosis and gangrene. Therefore, it is important to timely make the correct diagnosis and start treatment.
How do varicose veins develop?
The exact causes of this disease are not known. But the mechanism of how varicose veins develop is well understood.
The venous network of the lower extremities is represented by deep and peripheral veins, as well as communicating (perforating) vessels that connect them. Normally, blood flows through the veins to the heart, from peripheral to deep vessels.
This happens due to the muscular pump (contraction of the muscles of the lower extremities), the tone of the vascular wall and the work of the venous valves. The circulatory system is regulated by the vasomotor center in the brain.
However, violations of at least one of these links result in reverse blood outflow. At the same time, the peripheral vessels expand, the valves stop closing, which leads to even greater congestion of blood in the peripheral circulation.
Under blood pressure, the vein wall expands further, causing the vessels to lengthen and knots to form. Valve insufficiency increases, edema develops.
Compression of the peripheral nerves sends a signal to the brain about the need to increase the tone of the vessel wall. This increases the blood pressure in the deep vessels and the blood is pressed from them into the peripheral ones, causing them to expand even more. A vicious circle closes.
What causes varicose veins
The true cause of varicose veins is not known. However, it has been proven that a number of factors and physiological conditions contribute to its development.
Like:
- pregnancy (due to the compression of the veins in the abdominal cavity by the pregnant uterus, blood circulation in the lower extremities is complicated);
- Obesity;
- lack of exercise;
- Genetic predisposition (weak valves or decreased tone of the vessel walls);
- violation of hormonal balance (leads to an increase in blood viscosity and difficulty in outflow);
- Condition after operations (due to increased blood clotting and bed rest);
- Professions associated with a long stay in an upright position (on their feet).
In the case of any of these situations, it is necessary to take preventive measures to prevent the development of varicose veins. Especially if clinical manifestations are already present.
Symptoms of varicose veins
The first signs of varicose veins are:
- pain and heaviness in the lower extremities;
- swelling of the legs in the evening;
- The appearance of spider veins on the skin;
- visible strained veins under the skin;
- burning and itching in the affected area;
- Cramps in the muscles of the lower extremities, especially at night.
Pain with varicose veins appears and intensifies by the end of the day. They have a bursting, painful character. At the beginning of the disease, they disappear after rest, and therefore patients do not go to the doctor for a long time.
On examination, edema, pastosity of the legs, telangiectasia are revealed, strained trunks of veins, often painful, are palpated. How the skin of the legs with varicose veins looks like can be seen in the photo.
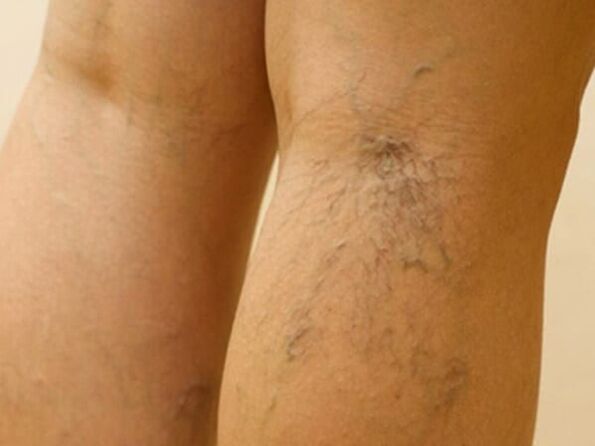
At the stage of severe decompensation, weakness, dizziness and fainting may appear. At the same time, trophic disorders become noticeable on the skin, ulcers, dermatitis and eczema develop. With a timely visit to the doctor, severe manifestations of varicose veins can be prevented.
Types of varicose veins
There are the following types of varicose veins:
- Varicose veins of the lower extremities (the most common variant);
- varicose veins of the upper extremities;
- pelvic varicose veins (including uterine varicose veins);
- varicose veins of internal organs (esophagus, stomach, intestines, etc. );
- varicose veins on the face.
The most studied type is varicose veins of the lower extremities. It is the most common and is usually what is meant when the disease is mentioned. Most patients do not know if internal varicose veins exist and how they manifest themselves until they encounter them.
Stages of development of varicose veins:
| stage of the disease | Clinical Manifestations |
|---|---|
| 1st stage | There are no symptoms, varicose veins are detected only on instrumental examination |
| 2 steps | Heavy leg syndrome, transient edema, spider veins on the skin |
| 3 steps | Persistent edema, pigmentation disorders of the skin, dense tense veins and knots are visible, trophic disorders in the form of eczema |
| 4 levels | There are trophic ulcers, dermatitis, necrosis |
The smaller the stage, the easier the treatment and the better the prognosis for healing.
Diagnosis of varicose veins
In addition to the examination data and characteristic complaints, a laboratory and instrumental examination of the patient is required to make the diagnosis.
laboratory diagnostics
What tests should be done for varicose veins:
- Complete blood count with advanced formula.
- Blood clotting tests:
- clotting time;
- prothrombin test;
- Determination of Antithrombin III, Protein S and C;
- determination of homocysteine levels;
- examination of the APTT index;
- Determining the level of the D dimmer;
- Determination of von Willebrand factor activity etc.
- blood biochemistry.
- hormone analysis.
- General urinalysis.
- functional tests.
Determining the state of the blood coagulation system is of crucial importance in the choice of treatment tactics and the prognosis of the course of the disease.
Instrumental diagnosis of varicose veins
Of the instrumental research methods used:
- ultrasound examination of veins;
- dopplerography;
- Ultrasound duplex scanning of veins (combination of ultrasound and dopplerography);
- angiography;
- Photoplethysmography (PPG);
- phlebography;
- venous occlusal plethysmography (VOP).
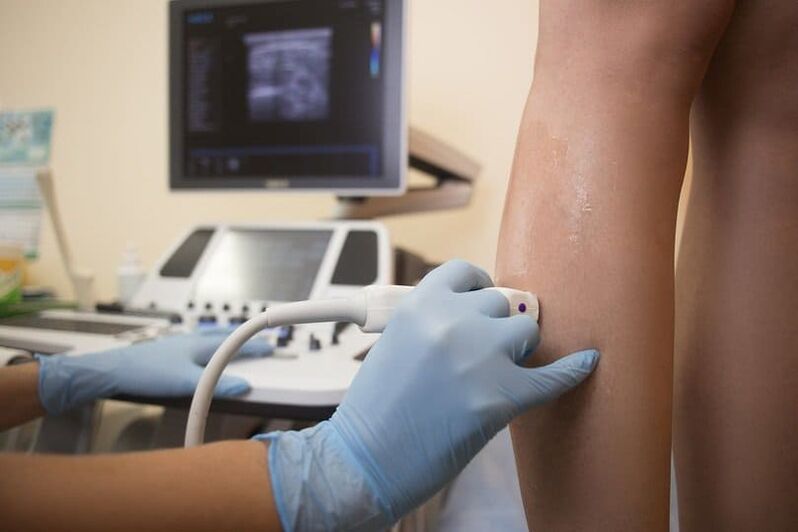
In this type of study, the thickness of the vessel wall is measured, the condition of the venous valves is examined, the presence or absence of reverse blood flow in the veins, etc. With the help of instrumental methods, it is possible not only to make the correct diagnosis, but also to accurately determine the stage of the disease.
Treatment of varicose veins
Combating varicose veins includes drug (conservative and surgical treatment) and non-drug methods. The choice of a particular option depends on the stage of the disease and the degree of its external manifestations.
Conservative treatment of varicose veins
Therapy of this disease included surgeons and phlebologists. At the first signs of the disease, you need to contact the doctors of these specialties. They confirm the diagnosis and, in this case, prescribe treatment for varicose veins.
In conservative therapy, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Antiplatelets used to thin blood and prevent blood clots;
- Anticoagulants of direct and indirect action to improve the rheological properties of blood and prevent its thickening;
- Phlebotonics to strengthen the vascular wall, herbal preparations with horse chestnut extract;
- anti-inflammatory drugs, if necessary (in case of inflammation in the vascular wall or surrounding tissues).
Most of these drugs are available both for oral administration (in tablets and capsules) and for external use (in the form of ointments, gels, creams). The doctor will tell you which form is most suitable for that patient, depending on the specific clinical situation.
Surgical treatment of varicose veins
Conservative therapy will help to completely cure the disease only in the early stages. In advanced cases and with signs of decompensation, surgical treatment of the varicose veins is necessary.
Surgical intervention may consist of removing the entire vein or just the affected area through incisions along the vessel or in the groin crease and popliteal fossa (depending on the specific vein and its location). But whenever possible, doctors try to perform a less traumatic procedure that causes coagulation of the affected vessel, leading to its complete obstruction.
Options for economical operations:
- sclerotherapy (insertion through a catheter into the lumen of the vessel of special sclerosing drugs that cause solid adhesions in it with their subsequent replacement with connective tissue);
- endovascular laser coagulation (coagulation of the inner cavity of the vessel with a laser pulse);
- High-frequency coagulation (adhesion of the vein walls by exposure to a high-frequency current impulse);
- Miniphlebectomy (removal of a vein or cutting it through multiple punctures in the skin).
When performing coagulation in different ways, the result is the same - after gluing the walls of the vessels, the cavity is gradually filled with connective tissue, with the development of a complete obstruction. In this case, blood movement continues through healthy vessels, bypassing the coagulated ones. Schemes for performing such operations can be seen in the video in this article.
Surgical methods have one undeniable advantage - the probability of recurrence is very small. In terms of risk versus effectiveness, less traumatic interventions are better. But the price for them in clinics is quite high.
Non-drug treatment of varicose veins
Strengthening the walls of blood vessels with varicose veins is quite possible without the use of tablets.
Of non-drug means for this use:
- therapeutic exercises (to stimulate the muscle pump);
- Compression stockings and elastic bandages (compression of the lower extremities stimulates blood ejection from the vessels, normalizes the function of the venous valves, strengthens the vascular wall).
Wearing compression stockings is recommended for all at-risk individuals, especially:
- pregnant woman;
- work standing all day;
- to all people during long flights on airplanes;
- Patients taking medicines that promote blood clotting;
- people with a sedentary lifestyle.
Prevention of varicose veins
Prevention of varicose veins is better to start before they appear. In addition, the recommended measures will help prevent other cardiovascular diseases.
Prevention Advice:
- give up all bad habits;
- Carefully monitor your diet (excluding fat, fried, smoked, sweet);
- strictly control your weight;
- Lead an active lifestyle (more walking, running, cycling, in-line skating, etc. );
- wear comfortable shoes with low heels;
- daily alternating shower;
- At the end of the day, take a 15-minute rest with your legs elevated.
These measures also help when varicose veins are identified – to prevent further progression of the disease and the development of complications.
Many are interested in whether it is possible to play sports with varicose veins. The attending physician will answer this question exactly, but in most cases you can play sports, except for the severe types associated with power loads.
Varicose veins are a common condition. Women suffer from it four times more often than men, which is due to the peculiarities of the hormonal background, pregnancy and a large list of women's professions, where the whole working day is on their feet.
However, timely prevention will help prevent the development of varicose veins in both men and women. The main thing is not to neglect the advice of a doctor and do not forget about the regularity of preventive measures.



















